Setting Up Your Page Information/Content
Contents
Set Up Your Page Information and Content
- Title Tag
- META Keywords Tag
- META Description Tag
- Headline Strategies
- Text Link Strategies
- Body Copy Strategies
- Related Pages
Page Information includes the Title, META Keywords and META Description tags. Page Content covers the Headline, Text Links and Body Copy.
How well you set up your Page Information and Page Content could mean the difference between low and high ranks on search engine results pages (SERPs).
When you make it into the coveted Top 10 positions, people start to notice your listings.
And then it's quality relevant content that gets the click from your visitors and compels them to explore your site.
Title Tag
- Weave your Specific Keyword into the Page Title at least once, no more than twice.
- Limit your Page Title to a maximum of 55 characters.
Your Page Title appears at the very top of a browser window. Most humans never see your Title once they're on your page!
Why?
Because they tend to first look at the headline of a page, not at the top of the window.
However, the Page Title plays a very important role.
Search engines give special emphasis to these words when ranking for relevance. And when they return search results to searchers, they display your Page Title, exactly the way you write it, as the link to your page.
See how the Page Title for this page on anguilla-beaches.com, "Top Cheap Anguilla Hotels and Accommodations," became a link?
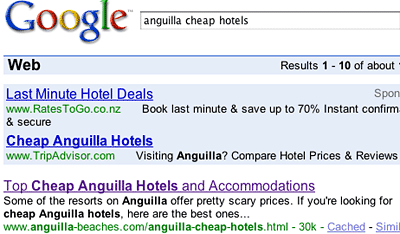
Since your Page Title is the first thing that humans will read in the listings, it must suggest something of value to the readers. It must compel them to click to your page to investigate further. "Top Cheap Anguilla Hotels and Accommodations" does its job well.
The Page Title is also used to create the Open Graph Title tag. The title will appear on a Facebook user's timeline when they Like the page, share it, or comment on it. Other social services also use Open Graph tags, widening your page's reach even more.
The format is always...
<title>Your Page Title</title>
Ensure that the tag is placed between the <head> and </head> tags.
Tips
-
You must have a Page Title. Solo Build It! will not allow you to upload the file if you do not have a title.
-
Place your Specific Keyword near the beginning (second or third word is ideal; fifth is the farthest).
-
If you use your Specific Keyword twice, use a variant of the keyword the second time. Try using the plural and singular forms of keywords (e.g., "restaurant" and "restaurants").
-
Capitalize the Page Title for a cleaner presentation. Do not use ALL CAPS, as they are harder to read and are considered shouting or screaming.
-
SBI! will not allow you to use a Page Title longer than 55 characters, including punctuation and spaces. (Google recently changed its results page layout, so making your title longer than 55 characters means that the last characters would not show in the result listing for the page.)
-
You cannot use HTML code (e.g., <strong> or <em>) in your Page Title. The code itself will display at the top of your browser window if you do.
-
Do not use special characters in your Page Title (e.g., "&") if you plan to use RSS/Blog It!. Some RSS readers have problems with these characters.
-
If you're using SBI!'s RSS/Blog It! module, keep in mind that subscribers will see the Page Title as the title in their readers, so make it descriptive.
META Keywords Tag
- Enter only your Specific Keyword.
Each of your site's pages must focus on one Specific Keyword.
Enter only your Specific Keyword in the Meta Keywords tag.
For the sample page from above, the owner entered this keyword... cheap Anguilla hotels. If you view the page's source code (on your browser's toolbar, select "View" and then "Source"), you'll see this...
<meta name="keywords" content="cheap Anguilla hotels">
The format is always <meta name="keywords" content="Specific Keyword">, as in the example above. Enter your keyword between the quotation marks at the end of the tag. Ensure that the META tag is between the <head> and </head> tags.
Tip
-
SBI! will warn you if you have forgotten to add the META Keywords tag.
META Description Tag
- Use your Specific Keyword at least once (but not more than twice).
- Create a compelling description of your page.
- Maximum 200 characters, including punctuation and spaces; 150 is better.
Think about your META Description as an advertisement you're writing for your page. But realize that your human visitors will not see it on your site's page.
Search engines often use your META Description tag to create the description in the search results page listing (unless they find some content on the page that will be a better description).
The Description forms the second half of what searchers see in an SE's listings. (Your Page Title forms the first half.)
The Description is also used to create the Open Graph Description tag. The description will appear on a Facebook user's timeline when they Like the page, share it, or comment on it. Other social services also use Open Graph tags, widening your page's reach even more.
So all the rules of good copywriting apply. Compel the reader to click to your page.
Make sure the Description is attractive, without being misleading. A gentle, good-natured tease will do well. Provide a lead-in to some information that your potential visitor can't live without.
But then don't disappoint when they land on your page.
Let's stay with the same sample page, Cheap Anguilla Hotels. Its META Description draws you in... "Some of the resorts on Anguilla offer pretty scary prices. If you're looking for cheap Anguilla hotels, here are the best ones..." This works. After all, who wants to blow all of their vacation budget on accommodation?

Tips
-
Don't repeat your Page Title. The reader will just see the same phrase twice in the listing. That's a waste of valuable "word real estate."
-
Don't overdo the use of your Specific Keyword. If you repeat it excessively, the SEs will penalize you. Use it at least once, though (twice, if it sounds natural). Blend one or two uses of your Specific Keyword with General Keywords and/or common synonyms. (Experiment a little.)
-
Tell the reader "what's in it for him/her."
-
Each niche's set of competitors and circumstances is different, so do not be afraid to experiment to see what works for you. A longer (165 characters max) description may work better for you. Having three variants of your Specific Keyword may be just right, or too many.
-
Never use ALL CAPS in your Description. It's considered yelling or screaming, and is usually seen as the sign of an amateur webmaster.
-
Put only one space between sentences, not two. This saves a character each time.
-
Never use quotes or non-standard characters (e.g., "&"). They can mess up an SE's listing, and also cause problems for some RSS readers.
-
If you're using SBI!'s RSS/Blog It! module, keep in mind that the first part of your page's Description is what your subscribers will see displayed in their readers.
Search engines don't seem to weight the Description very heavily in their relevance rankings, so concentrate your writing efforts on "getting the click."
Additional Page-Building Tip
If you do not want a page indexed by the engines, add <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> (also called a NOROBOTS tag) in the <head> section, like this...
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
When SBI! sees that tag, it will not add the page to the sitemap XML file. And if the engines somehow find the page, they will not spider it. If you do add it, remember not to put the page in your RSS feed.
This is especially useful for a landing page for a newsletter ad, for example. The search engines will not see it as thin content and penalize you.
Headline Strategies
Every page starts with a headline. Your "top-of-the-page" headline is the first thing that humans will read on your web page. Catch the attention of their scanning eyes. Draw your visitors into the rest of your page... and lead them to your links!
- Select the headline size, click where you want the headline to be, and type the words. Add any styling and line breaks while typing, or afterwards by selecting the text.
- If you're hand-coding, enter the applicable HTML tags and type your headline words between the tags.
How do you write a headline?
It's not complicated. Split your META Description contents (which you wrote earlier) in two.
Use the first part (the most important part for the SEs) for the headline. Then use the rest of the Description as the beginning of your Body Copy's opening paragraph (see below).
You may have to re-work the words a bit so that it all "hangs together" well.
An Example From Anguilla-Beaches.com
This Description...
"Anguilla is the most special Caribbean vacation. Here are our most magical, must-do moments captured in these Anguilla photos."
... is chopped up and re-arranged into this headline...
Caribbean Vacation
Magic Moments and
Special Anguilla Photos
This example works on two levels...
1) For human visitors...
The headline is intriguing. The phrase "Magic Moments" suggests extraordinary events. It's short and punchy, which is especially appealing to scanners.
The headline also leads into the opening paragraph of the body copy nicely...
"Anguilla is a magical Caribbean vacation island, in a beautiful sea. Everything that you see and experience is special in its own way."
2) For search engines...
The headline contains the page's Specific Keyword, "caribbean vacation." (This will please Analyze It!.)
Many SEs give more weight to the keywords in your headlines, especially your H1 headline at the top of the page, than to the keywords in your body copy. The engines interpret them as being the most important copy on the page. Only the Page Title is more important.
Some SEs do not use your description in their listings on search results pages. Instead, they use a content snippet from your web page to construct the description in your listing.
That's why it's important to use roughly the same material in your description and your headline/opening paragraph, and to keep your headline as short as possible (without sacrificing the "punch").
Headline Tag Format
Headline tags come in several sizes, from the largest (h1) to the smallest (h6). H4 is usually the same size as your normal text.
You can add styling to headlines by styling them in your CSS file.
You can also align headlines to left, right or center, setting it in the CSS file.
The correct format for an h1 tag is <h1>Your Headline Here</h1>.
Tips
-
Keep the headline shorter than 80 characters; 40 is best. (Spaces and punctuation count as characters.)
-
If your headline is longer than one line, "break it" so that the two (or more) lines are about equal length, especially if you center it. Use the <br> HTML tag to insert a single line break (e.g., Caribbean Vacation<br>).
-
Include your Specific Keyword once, not more than twice.
-
Use headlines for more than just "top-of-the-page" announcements. Use smaller (H2 and H3 size) headings to break up a long page, especially if you're introducing a new, important thought.
-
Use Capital Case (if you wish) to give your headline more visual impact. Do not use ALL CAPS, as this is perceived as shouting or screaming, and is seen as a sign of an amateur webmaster.
-
Normally, headlines do not contain periods, as they are not complete sentences. However, they may have commas, dashes, question marks or exclamation marks.
Text Link Strategies
Text links belong right in the natural flow of the content, woven seamlessly into paragraphs. That's why they're called "in-context" text links.
- Create a link. Add the destination URL, the anchor text, and whether to open in a new window.
- If you're creating links manually, use the correct link format and double-check that you added the close tag </a>.
Use text links to smoothly direct your visitors to valuable related pages within your site or to lead them to your monetization models.
Wherever possible, do not relegate your income-producing links to a listing at the end of your Tier 2 or 3 page.
Some visitors will assume that a sales pitch is coming next and they will ignore these links (or even worse, exit the site).
Text links also help search engines to deep-spider your site. Make it easier for them to do their job!
Your Tier 2 page links have three goals...
-
First choice is a click to one of your Tier 3 pages that provide more details on the subject, or to related Tier 2 pages.
-
Second choice is to get the click to your income-generation source (always open a new window for these, so that your page remains open underneath).
-
Third choice is a click back to the home page.
Your Tier 3 page links have four goals...
-
First choice is to get the click to your income-generation source (always open a new window for these).
-
Second choice is a click back to the related Tier 2 page.
-
Third choice is a click to other related Tier 3 pages on your site.
-
Fourth choice is a click to a complementary website. (Always open a new window for these links.)
An Example From anguilla-beaches.com

Text Link Format
To link to other sites, you must use absolute URLs. The correct format for a text link to another site is...
<a href="https://www.domainname.com/file-name.html" target="blank">the "anchor text" of the link</a>
When linking to pages in your own site, you want to be able to test the links before you upload the page. To do that, use relative URLs. To link to a page within your own site, the correct format is...
<a href="file-name.html">the "anchor text" of the link</a>
Tips
-
Always link to a page in your own site as a relative URL (e.g., "anguilla-villas.html"). When you upload your HTML page, SBI! automatically converts your relative links to absolute ones with the "www" (e.g., https://www.yourdomainname.com/anguilla-villas.html").
-
To prevent typos, copy-and-paste the URL when you enter a new off-site (outbound) URL.
-
If you're linking to an outside site, have the link open a new window, so that your page remains open underneath. Use target="_blank" to do this. If you're linking within your site (i.e., to another page in your site), do not have the link open a new window. It will annoy your visitors.
-
When you preview the page, test the link to make sure it goes where you want it to go.
Body Copy Strategies
Your Body Copy is where you "tell your story."
- Type your text directly into the window and format it as you go by clicking on buttons to align or style the text, add tables and lists, and add line breaks and horizontal rules to add white space.
- If you're hand-coding, type your text and add all the styling and alignment tags, along with break and rule tags.
How long should a page be?
Provide the high quality information your visitors seek in a way that respects their time. So, how long should your page be?
Too short or too long pages cause people to exit a site quickly. Make the length "just right" for your target audience. Aim for at least 400 words (we recommend that you write 500-600 per page).
As always, consider both kinds of readers... human and spider.
For your human readers...
Start your body copy strongly, for two reasons...
1) Compel your pre-visitor to click on your search engine listing. A content snippet (and your main headline) will appear in some SE search listings, so it needs to do the job of a good meta Description.
2) Compel your page visitor to continue down the rest of your page to your income-generating links.
OVERdeliver great content. Establish the main benefits of reading this particular page right away. In short, answer the "What's in it for me?" question that every visitor asks when arriving at a new page.
Create an enjoyable reading environment for your visitors... a friendly, informed tone, active verbs, short sentences, no more than 4 or 5 lines per paragraph, etc. (See Make Your Content PREsell! for additional strategies.)
For the Search Engines...
Think like a search engine that's checking for certain "on-page" ranking criteria...
The nearer your Specific Keyword is to the beginning of a page, the higher the SE scores it. So include your Specific Keyword in the opening sentence of your page, if it doesn't read awkwardly to have it there.
Use the Specific Keyword early and a bit more at the top of your content and also in the closing paragraph. Then weave it throughout the rest of your copy.
This "scatter pattern" should look like an hourglass... wider (i.e., more frequent) on the top and bottom, and narrower (less frequent, but still present) in the middle of the page. Keep usage reasonable, though. The SEs look for excessive use of keywords as a sign of "keyword spamming."
A Good General Guideline
Include your Specific Keyword a bit more than "good writing" normally dictates. In other words, look for ways to repeat it slightly more often than you would ordinarily.
Start blending in your General Keywords, too, so that you can score for word combos (i.e., Specific Keyword + General Keyword). Choose General Keywords that a searcher is most likely to associate with your Specific Keyword. And mix in some common synonyms/variations of your Specific Keyword.
Also try changing your approach somewhat from page to page. Experiment with different numbers, frequencies and patterns of keywords until you find what works best.
But stick to the topic of the page. Do not, ever, get off-target. Keep each page focused on material related to your Specific Keyword. Never introduce a second topic to a page -- no mixed messages. Make each page focus purely on its "Specific Keyword topic."
The more you laser-beam on a single topic, the better you'll do with the search engines.
Bottom Line
Always keep the three major roles of your content in mind...
-
Get the click -- Make it compelling for your visitor to click on links to another page of your site, or, even better, to one of your income-generating opportunities (e.g., merchant-partner, store, sales site).
-
Get the traffic -- scatter your Specific Keyword, as well as General Keywords and common synonyms, throughout the page, as discussed above.
-
Lead the search engine spiders through to your Tier 3 pages. Each Tier 2 should have links to 5-15 Tier 3 pages (which feature content related to the Tier 2 topic). The spiders follow these links and put your Tier 3s into their databases.
This means that your potential visitors can find you for more and more Specific Keywords, which brings you ever more traffic!
Tips
-
You can add stop words (such as an, or, and, in, of, etc.) to awkward-sounding keywords to improve readability, if you wish. SEs skip over stop words.
However, if you decide to do this, you may want to write the page without the stop words, save and upload it, then run Analyze It!. If the page passes, edit your page to add the stop words, then re-upload and build the page without running Analyze It! again. If you do test your page again, Analyze It! will not pass it.
For a complete list of stop words and how to use them properly, see this forum post.
-
Left-align your content. Short copy can be centered for effect, but use this sparingly. Using full (or justified) alignment (aligned along the left and right) makes it more difficult to read the text by eliminating line length cues.
-
Break up the page by using headlines, images, videos, break (<br>) tags, and horizontal rules (<hr>).
-
Always add hand-coded HTML code carefully. For example, if your page looks weird (all bold, all a certain color, etc.), you have forgotten to close a tag.
After you attract targeted visitors to this page, after you convince them to read more deeply, it's your words that will make or break your success.
Related Pages
You can display a series of pages with related content at the bottom of any page of your site. You'll do that with the code provided below.
You can't use it with a Sitewide Dot, however. If you did that, all the pages of your site would have links to the same related pages.
Add the following code to the end of the text of content pages of your site...
***RELATED_PAGES
category="Your-Category"
count=6
orientation="vertical"
thumbnail=false
headline="Your Headline"
***
Creating Categories
Before you (re)build any pages with the Related Pages code on them, go to the Related Pages Library and create one or more categories.
Once you do that, assign all of your already published pages to one of the categories. A page can be in more than one category.
Once you have all of your pages in categories, it's time to add the code above to your pages and upload them again.
Code Changes
Do not remove any of the asterisks (*) or the words RELATED_PAGES. If you change either, the code will not work and no related pages will appear on the page.
category="Your-Category"
If you select one of your categories for the current page, the live page will show related pages from that category. If you do not enter a category in the code (category=""), this page will show only related content from the category you assigned to this page in the Related Pages Library.
Categories must be all one word, which includes hyphenated words.
count=6
This tells the system how many related pages to add to the Related Pages section where you add the code. The higher the number, the more pages. Depending on the orientation (discussed next), this could result in a long Related Pages section.
orientation="vertical"
You can have the various links displayed vertically (down the page) or horizontally (across the page, wrapping to a second line if there isn't enough room). On mobile devices, one or two will display per row.
If you select "horizontal," then you must set "thumbnail" (next) to true.
thumbnail=false
As noted above, if the orientation is horizontal, the only option here is "true" (show thumbnail images). If you set the orientation to vertical, you can display thumbnails (one per related page) or not display them ("false").
headline="Your Headline"
The H2 headline will appear above the first related page in the section (vertical orientation) or the first row of related pages (horizontal).
If your category is about pizza, you might use "More Pages About Pizza" as the headline.
You can choose to have no headline (not recommended) by leaving the headline line empty (headline="").
